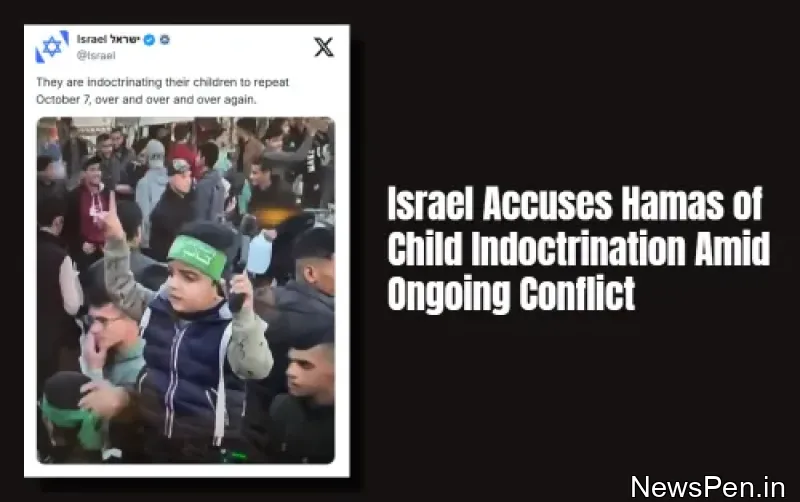
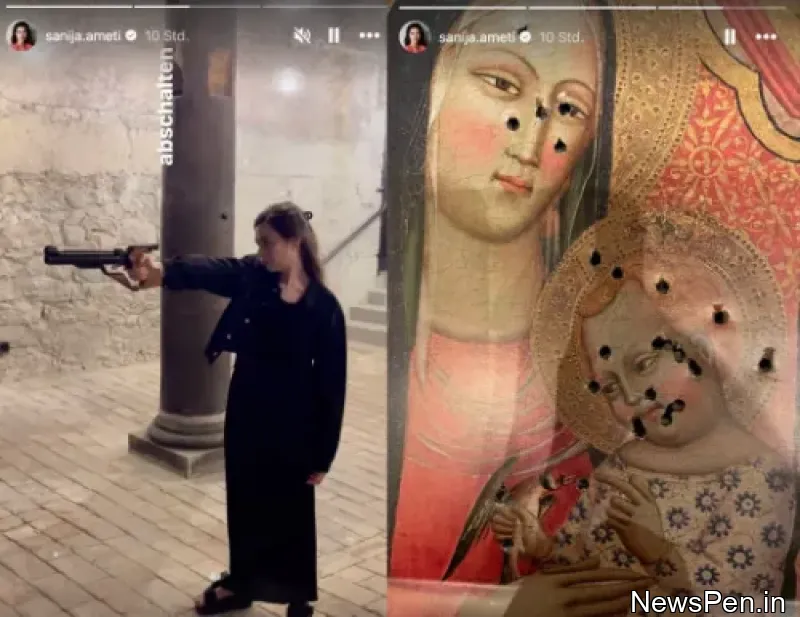
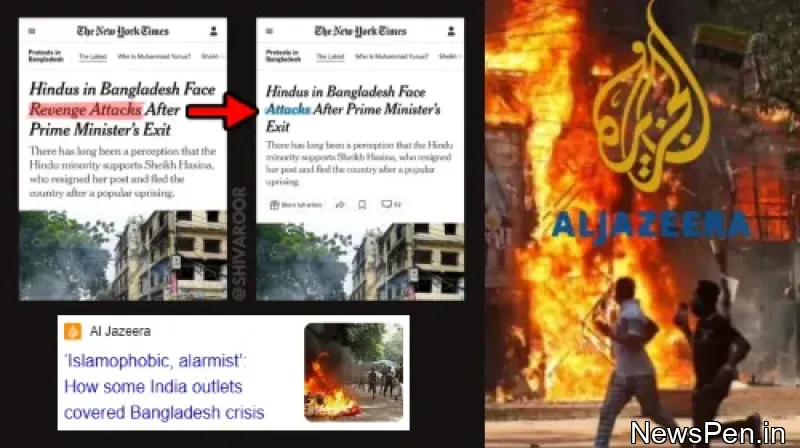
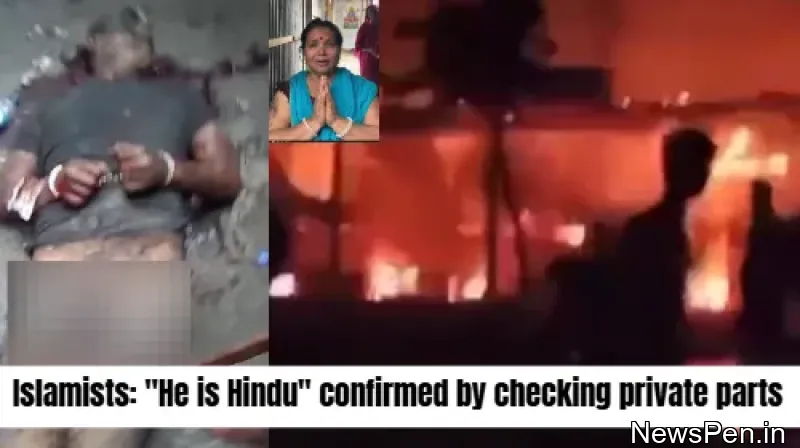
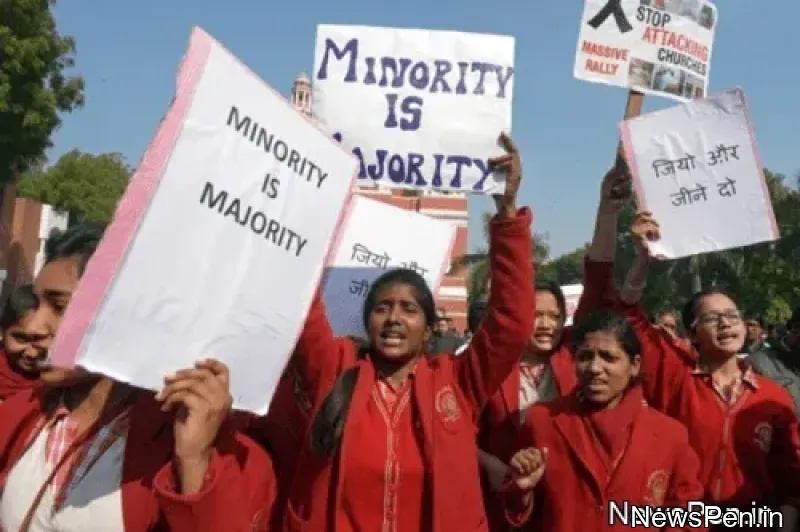
Minorities in India can now be identified on a state-by-state basis

The national government has remained deafeningly silent on Hindu concerns for decades. By redefining the concept of minorities, the administration has made history.
The 1992 Act Establishing a National Commission for Minorities has been revoked. The Centre has told the Supreme Court that under Articles 29 and 30 of the Constitution, Hindus can be classified as a minority.
The Centre has stated that minorities should be identified on a state-by-state basis rather than on a national one. In Sikkim, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Punjab, Kashmir, and Lakshadweep, Hindus are a minority.
Hindus in these states might be deemed minorities, according to the Centre.
State governments can now offer minority status to any religious or linguistic community, including Hindus, according to the Union government's submission to the Supreme Court.
The Supreme Court had requested the Union government's answer in a petition seeking orders for the creation of state-level standards for recognising minorities. The petition claimed that Hindus are a "minority" in six Indian states and three Union Territories, but that they were unable to take advantage of minority-specific initiatives.
DISCLAIMER: The news content above is submitted by Newspen users and also scrapped from external websites.